Case study:Barking Creekmouth
Project overview
| Status | Complete |
|---|---|
| Project web site | |
| Themes | Fisheries, Habitat and biodiversity, Social benefits, Urban |
| Country | England |
| Main contact forename | Scarr |
| Main contact surname | Toni |
| Main contact user ID | User:Ascarr |
| Contact organisation | Environment Agency |
| Contact organisation web site | http://www.environment-agency.gov.uk |
| Partner organisations | |
| Parent multi-site project | |
| This is a parent project encompassing the following projects |
No |
Project summary
Previous site use/issues
- underused and undervalued area of greenspace, owned by the Environment Agency, adjacent to the Barking Barrier.
- The terrestrial habitat consisted of species poor grassland with patches of scrub and Japanese knotweed. Areas which would have supported saltmarsh species were encased in riprap covered in bitumen and had be historically land raised.
- The foreshore in this area is important for overwintering birds such as teal, shelduck, tufted duck, wigeon, gadwell, shoveler, pintail, little grebe. Common whitethroat, sandmartins and linnet has been seen breeding in the area a pair of oyster catchers were also recorded breeding in 2000. Saltmarsh and mudflat UK BAP habitat is very important for these types of fauna and also flora.
- Barking Creek is recognised as a valuable feeding and refuge area for a variety of fish species, flounder, eel, smelt, sea bass in both their adults and juveniles life stages. These utilise the full range of sub, intertidal and saltmarsh habitats for foraging and refuge.
- There was limited amenity use, lack of seating areas, views from site obstructed by flood defences and no wheelchair access to site.
- Failing flood defences.
Monitoring surveys and results
Enhancements
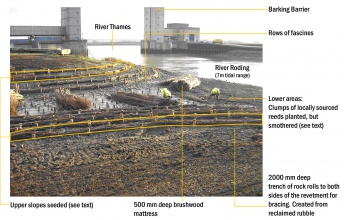
- Breach of existing defence and creation of tidal backwater providing increased flood storage and wildlife habitat.
- The backwater area and new reedbeds represent a new, highly valuable feeding and refuge area for fish. Recent studies have shown that both juvenile and adult fish move into these areas as soon as they are inundated. They feed extensively on the invertebrates present within the reedbeds. Such habitats are increasingly thought to significantly enhance the juvenile survival of commercially important fish such as bass. The Thames Estuary is now recognised as an important nursery area for this species.
- Retreat and renewal of flood defences to provide current standards of flood risk allowing for changes due to climate change.
- New site entrance and access route through site.
- Creation of new seating and viewing areas.
- Interpretation boards installed with the aid of Lee Rivers Trust and local school children helped design the boards
Lessons learnt
The sites were important for overwintering birds: teal, shelduck, tufted duck, wigeon, gadwell, shoveler, pintail, little grebe, common whitethroat, sandmartins, oyster catchers and linnet. Peregrine falcons also use the site.
Barking Creek is recognised as a valuable feeding and refuge area for a variety of fish species, flounder, eel, smelt, sea bass in both their adults and juveniles life stages. These utilise the full range of sub, intertidal and saltmarsh habitats for foraging and refuge.
Image gallery
|
Catchment and subcatchmentSelect a catchment/subcatchment
Catchment
Subcatchment
Other case studies in this subcatchment: Barking Creek near A13, Chambers Wharf, Cuckolds Haven Nature Area, Greenwich Peninsula, Lower River Roding Regeneration Project, Mill Pool, Saving Chiswick Eyot, Wandsworth Riverside Quarter
Site
Project background
Cost for project phases
Reasons for river restoration
Measures
MonitoringHydromorphological quality elements
Biological quality elements
Physico-chemical quality elements
Any other monitoring, e.g. social, economic
Monitoring documents
Additional documents and videos
Additional links and references
Supplementary InformationEdit Supplementary Information
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||