Case study:River Stour at Glen's weir (Throop fisheries)
This case study is pending approval by a RiverWiki administrator.
Project overview
| Status | Complete |
|---|---|
| Project web site | |
| Themes | Fisheries |
| Country | England |
| Main contact forename | Nick |
| Main contact surname | Elbourne |
| Main contact user ID | |
| Contact organisation | River Restoration Centre |
| Contact organisation web site | |
| Partner organisations | |
| Parent multi-site project | |
| This is a parent project encompassing the following projects |
No |
Project summary
The works completed by the Environment Agency contributed to the Stour achieving good ecological status under the Water Framework Directive.
Aims were to:
-increase flow and natural scouring, to encourage self-cleaning of gravels
-enhance existing spawning areas up and downstream of Glens Weir
-increase parr and barbell habitat
-re-instate collapsed banks, re-profile weir pool to increase pool habitats
-provide fly refuge area
-reduce cattle poaching
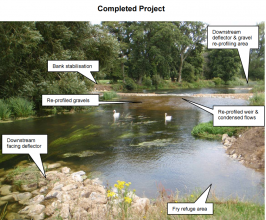
Dredging in the 1970’s removed thousands of tonnes of gravel to reduce flood risk. This eliminated large areas of spawning habitat for many species of fish. In some places the river has re-naturalised, however routine dredging still takes place downstream as part of the Christchurch flood alleviation scheme. The project aimed to provide new spawning habitat in a previously dredged area. The location was selected based on data gathered by the Environment Agency, The Barbel Society and Ringwood & District Angling Association. Pre-project monitoring work was completed, with post-project monitoring taking place with the help of the RDAA and Barbel Society through catch data, electrofishing and red count data. Around 600 tonnes of Portland stone was used to complete the works; bank stabilisation, old weir structure, flow deflectors and in channel re-profiling. The area was also fenced to prevent cattle poaching, with a gate to allow angler access.
The works have lead to increased flows over the spawning area, and the creation of holding features for larger adult fish. Over 100m of river habitat has been restored. In the past the Stour has often been seen as second best compared with neighbouring rivers but this is now changing.
Monitoring surveys and results
Lessons learnt
Catchment and subcatchment
Edit the catchment and subcatchment details
(affects all case studies in this subcatchment)
Site
| Name | |
|---|---|
| WFD water body codes | |
| WFD (national) typology | |
| WFD water body name | |
| Pre-project morphology | |
| Reference morphology | |
| Desired post project morphology | |
| Heavily modified water body | |
| National/international site designation | |
| Local/regional site designations | |
| Protected species present | |
| Invasive species present | |
| Species of interest | |
| Dominant hydrology | |
| Dominant substrate | |
| River corridor land use | |
| Average bankfull channel width category | |
| Average bankfull channel width (m) | |
| Average bankfull channel depth category | |
| Average bankfull channel depth (m) | |
| Mean discharge category | |
| Mean annual discharge (m3/s) | |
| Average channel gradient category | |
| Average channel gradient | |
| Average unit stream power (W/m2) |
Project background
| Reach length directly affected (m) | |
|---|---|
| Project started | |
| Works started | |
| Works completed | |
| Project completed | |
| Total cost category | |
| Total cost (k€) | |
| Benefit to cost ratio | |
| Funding sources |
Cost for project phases
| Phase | cost category | cost exact (k€) | Lead organisation | Contact forename | Contact surname |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Investigation and design | |||||
| Stakeholder engagement and communication | |||||
| Works and works supervision | |||||
| Post-project management and maintenance | |||||
| Monitoring |
Reasons for river restoration
| Mitigation of a pressure | |
|---|---|
| Hydromorphology | |
| Biology | |
| Physico-chemical | |
| Other reasons for the project |
Measures
Structural measures
| |
|---|---|
| Bank/bed modifications | |
| Floodplain / River corridor | |
| Planform / Channel pattern | |
| Other | |
Non-structural measures
| |
| Management interventions | |
| Social measures (incl. engagement) | |
| Other | |
Monitoring
Hydromorphological quality elements
| Element | When monitored | Type of monitoring | Control site used | Result | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before measures | After measures | Qualitative | Quantitative | |||
Biological quality elements
| Element | When monitored | Type of monitoring | Control site used | Result | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before measures | After measures | Qualitative | Quantitative | |||
Physico-chemical quality elements
| Element | When monitored | Type of monitoring | Control site used | Result | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before measures | After measures | Qualitative | Quantitative | |||
Any other monitoring, e.g. social, economic
| Element | When monitored | Type of monitoring | Control site used | Result | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before measures | After measures | Qualitative | Quantitative | |||
Monitoring documents
Image gallery
Additional documents and videos
Additional links and references
| Link | Description |
|---|
Supplementary Information
Edit Supplementary Information