Case study:Eden Crayfish Restoration Project
Project overview
| Status | In progress |
|---|---|
| Project web site | http://trust.edenriverstrust.org.uk/white-clawed-crayfish-page-3.html |
| Themes | Economic aspects, Fisheries, Habitat and biodiversity, Land use management - agriculture, Monitoring, Social benefits, Water quality |
| Country | England |
| Main contact forename | Joanne |
| Main contact surname | Backshall |
| Main contact user ID | User:Joannebackshall |
| Contact organisation | Eden Rivers Trust |
| Contact organisation web site | http://www.edenriverstrust.org.uk/ |
| Partner organisations | Defra, Environment Agency |
| Parent multi-site project | |
| This is a parent project encompassing the following projects |
No |
Project summary
This project will improve the habitat and water quality of rivers within the Eden catchment in Cumbria. The River Eden is of international importance for its wildlife and is designated as a Special Area of Conservation (SAC). It supports many significant species including white-clawed crayfish, salmon, trout, eel, bullhead, lamprey, otter, water vole, invertebrates of river shingle and water crowfoot. The Eden is the best remaining stronghold of the endangered white-clawed crayfish, which is threatened and declining across the UK and Western Europe.
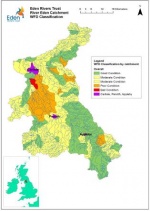
The Eden catchment comprises 98 water bodies. Under the Water Framework Directive (WFD) classification 59% of these fail to achieve Good Ecological Status and none of them are in “high” condition.
Problems within the Eden are due to agriculture, sewage, septic tanks, urbanisation, invasive species and poor quality habitats along and within rivers.
The project will restore more natural features in and around rivers and reduce the impact of diffuse pollution arising from agriculture. It aims to protect and expand populations of white-clawed crayfish as well as those of other valued river species. This will be achieved by installing riverside fencing (20 km), planting riverside trees (6,000), producing 20 farm assessments in areas of crayfish populations, carrying out improvement work on 20 farms to reduce diffuse pollution and carrying out in-stream habitat improvements at 5 locations.
Community Involvement - There will be a greater understanding and stewardship of the river environment amongst farmers and other land owners, volunteers and the general public.
Monitoring surveys and results
Annual juvenile salmonid electro-fishing surveys - see Eden Rivers Trust website for published reports.
Annual white-clawed crayfish manual hand search surveys - see Eden Rivers Trust website for published reports.
Fixed point photography monitoring of river habitat improvement projects (on-going - see examples under Monitoring below).
Repeated individual farm assessments with advice on reducing diffuse pollution, including farm infra-structure improvements where applicable (confidential to the land owner/tenant). A proportion will be reassessed at the end of the project.
Lessons learnt
Image gallery
|
Catchment and subcatchmentSelect a catchment/subcatchment
Catchment
Subcatchment
Site
Project background
Cost for project phases
Reasons for river restoration
Measures
MonitoringHydromorphological quality elements
Biological quality elements
Physico-chemical quality elements
Any other monitoring, e.g. social, economic
Monitoring documents
Additional documents and videos
Additional links and references
Supplementary InformationEdit Supplementary Information
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||