Case study:Little Don Catchment Case Study: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Project overview | {{Project overview | ||
|Status=Complete | |Status=Complete | ||
|Themes=Environmental flows and water resources | |Themes=Environmental flows and water resources | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
|Contact organisation url=https://www.catchmentbasedapproach.org/index.php?option=com_k2&view=item&layout=item&id=29&Itemid=244 | |Contact organisation url=https://www.catchmentbasedapproach.org/index.php?option=com_k2&view=item&layout=item&id=29&Itemid=244 | ||
|Multi-site=No | |Multi-site=No | ||
|Project picture=River Don map.png | |||
|Project summary=**Brief Outline of Scheme | |||
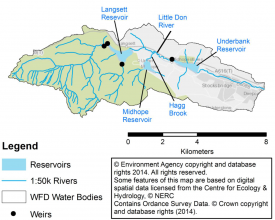
The Little Don rises in the Peak District National Park and joins the River Don just south of Stocksbridge town, a river length of about 20km. Flow in the watercourses are heavily regulated and managed by three reservoirs and several smaller impounding weirs. The reservoirs are operated by Yorkshire Water, with Langsett and Midhope reservoirs being operated for water storage, and Underbank reservoir for a compensation flow release. | |||
Langsett and Midhope reservoirs modify the downstream flow regimes by buffering the range and magnitude of flows. As a result the baseflow is lower than would be expected naturally and the timing and magnitude of autumn/winter high flows is dependent on the levels in the reservoirs during this time. A compensating flow is released from Underbank reservoir (the bottom reservoir of the group), although analysis of catchment inflows and rainfall patterns has shown this to be too high, a legacy of the industrial use of the Don catchment. Other Yorkshire Water reservoir compensation flow release trials have demonstrated that modifying flows to more naturally flow regimes can improve the quantity and diversity of the ecological community. The Little Don is defined as a Heavily Modified Water Body (HMWB) under the Water Framework Directive and assessed at moderate ecological potential, with an objective to improve to good ecological potential by 2027; | |||
this WFD objective is the main driver for the scheme. | |||
Barriers along the Little Don have been observed to significantly reduce ecological connectivity with large proportions of the watercourses under-used by trout and other fish. Whilst the barriers restrict the movement of coarse sediment, studies were inconclusive on the extent of the problem. Additional pressures within the catchment include water pollution (including minewater discharges) and invasive non-native species (such as the New Zealand mud snail). | |||
|Project title=Little Don Catchment Case Study | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{Image gallery}} | {{Image gallery}} | ||
Revision as of 18:49, 14 March 2018
This case study is pending approval by a RiverWiki administrator.
Project overview
| Status | Complete |
|---|---|
| Project web site | |
| Themes | Environmental flows and water resources |
| Country | England |
| Main contact forename | sarah |
| Main contact surname | Hyde |
| Main contact user ID | |
| Contact organisation | Environment Agency |
| Contact organisation web site | http://https://www.catchmentbasedapproach.org/index.php?option=com k2&view=item&layout=item&id=29&Itemid=244 |
| Partner organisations | |
| Parent multi-site project | |
| This is a parent project encompassing the following projects |
No |
Project summary
- Brief Outline of Scheme
The Little Don rises in the Peak District National Park and joins the River Don just south of Stocksbridge town, a river length of about 20km. Flow in the watercourses are heavily regulated and managed by three reservoirs and several smaller impounding weirs. The reservoirs are operated by Yorkshire Water, with Langsett and Midhope reservoirs being operated for water storage, and Underbank reservoir for a compensation flow release. Langsett and Midhope reservoirs modify the downstream flow regimes by buffering the range and magnitude of flows. As a result the baseflow is lower than would be expected naturally and the timing and magnitude of autumn/winter high flows is dependent on the levels in the reservoirs during this time. A compensating flow is released from Underbank reservoir (the bottom reservoir of the group), although analysis of catchment inflows and rainfall patterns has shown this to be too high, a legacy of the industrial use of the Don catchment. Other Yorkshire Water reservoir compensation flow release trials have demonstrated that modifying flows to more naturally flow regimes can improve the quantity and diversity of the ecological community. The Little Don is defined as a Heavily Modified Water Body (HMWB) under the Water Framework Directive and assessed at moderate ecological potential, with an objective to improve to good ecological potential by 2027; this WFD objective is the main driver for the scheme.
Barriers along the Little Don have been observed to significantly reduce ecological connectivity with large proportions of the watercourses under-used by trout and other fish. Whilst the barriers restrict the movement of coarse sediment, studies were inconclusive on the extent of the problem. Additional pressures within the catchment include water pollution (including minewater discharges) and invasive non-native species (such as the New Zealand mud snail).
Monitoring surveys and results
Lessons learnt
Image gallery
|
Catchment and subcatchment
Site
Project background
Cost for project phases
Reasons for river restoration
Measures
MonitoringHydromorphological quality elements
Biological quality elements
Physico-chemical quality elements
Any other monitoring, e.g. social, economic
Monitoring documents
Additional documents and videos
Additional links and references
Supplementary InformationEdit Supplementary Information
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||