Case study:Assessing the habitats outcomes of Floodplain Forest restoration: the case study of the floodplain forest at the Ouse Valley Park: Difference between revisions
NataliaLinde (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (28 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Case study status | |||
|Approval status=Approved | |||
}} | |||
{{Location | |||
|Location=52.07148747465287, -0.8315277099609375 | |||
}} | |||
{{Project overview | {{Project overview | ||
|Status= | |Status=Complete | ||
|Project web site url=www.theparkstrust.com/parks/floodplain-forest | |||
|Themes=Environmental flows and water resources, Habitat and biodiversity, Hydromorphology, Monitoring, Water quality | |Themes=Environmental flows and water resources, Habitat and biodiversity, Hydromorphology, Monitoring, Water quality | ||
|Country=England | |Country=England | ||
| Line 8: | Line 15: | ||
|Contact organisation=Cranfield University | |Contact organisation=Cranfield University | ||
|Contact organisation url=www.cranfield.ac.uk/about/media-centre/news-archive/news-2014/floodplain-restoration-project.html | |Contact organisation url=www.cranfield.ac.uk/about/media-centre/news-archive/news-2014/floodplain-restoration-project.html | ||
|Partner organisations=The Parks Trust, Environment Agency, Hanson Cement | |Partner organisations=The Parks Trust, Environment Agency, EPSRC (Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council), Hanson Cement | ||
|Multi-site=No | |Multi-site=No | ||
|Project summary=The | |Project picture=Floodplain Forest 2.jpg | ||
|Project summary=The Manor Farm Floodplain Forest and its associated PhD research project is a best practice example of bringing together industry (Hanson), a charitable body (The Parks Trust), non-departmental public body (Environment Agency) and academia (Cranfield University). The Parks Trust (land owner) joined forces with Hanson (quarry operator) with the vision of creating this new floodplain forest landscape along of a 1 km reach of the River Great Ouse. It was the first project of its kind in United Kingdom where planning permission was obtained specifically for the creation of a floodplain forest habitat. | |||
The Parks Trust owns over 2000 hectares of parkland around Milton Keynes and continually seeks to improve their parks by providing new facilities, increasing biodiversity and enhancing habitats. The Trust joined with Cranfield University to establish a PhD research project to develop a hypothesis-driven adaptive monitoring framework for assessing the environmental outcomes of the Floodplain Forest, as a case study with application to ecological management. Outputs of this research have enhanced understanding of the aspects to consider when assessing floodplain forest re-creation/restoration and have been used to develop guidelines for land managers based on a long-term monitoring approach. These management guidelines will be applicable to other similar restoration projects. | |||
Community Involvement - bird-watching areas and information boards provided to encourage local interest in the area. | |||
|Monitoring surveys and results=The Parks Trust engaged Cranfield University to help establish a monitoring and evaluation strategy for the floodplain forest. As well as monitoring environmental variables the Trust will instigate market research and community engagement programmes to assess the effect of the developing habitat on how local people and visitors from further afield use and perceive the site. | |||
Cranfield University aimed to assess the habitat outcomes in the floodplain forest after quarry works finished. We have designed an adaptive monitoring framework in order to assess key variables (i.e. creating a baseline for further comparisons over time after restoration works finished). The key variables selected for restoration appraisal are soil, water table, vegetation, water quality and topography. We complement the AMF with a hypothesis (The ratio between vegetation associated with wet and dry soils within the floodplain forest and its associated river is determined by the site topography and the water table level) and study the water table level interaction with tree species in a glasshouse experiment. Results gathered in the experiment will be extrapolated to the field to assess the suitable habitats planting according to water table availability and topography in the floodplain forest. | |||
|Lessons learn=The project has increased the capacity and flood retention capacity of the floodplain by removing a volume of around 700,000 tonnes of mineral reserves. Some of this volume has been replaced by standing water but under non-flood conditions the standing water lies at lower level that the former ground. | |||
The project has also created better connection between the River Great Ouse and the pre-existing and new channels that have been created in the site. As the river level rises, water can flow into the site (i.e. floodplain) via these channels, thereby receiving floodwater that would previously have put pressure on more developed/built-up areas further down the Ouse Valley, such as Newport Pagnell which has a number of known flood risk areas near the River Ouse. | |||
The complex of channel sand low-lying landforms within the site, including gravel banks, sand bars and small islands provides a varied floodplain habitat that will mature into a diverse ecosystem supporting a wide range of plants and insects, amphibians, birds, fish and mammals such as otter and water vole. The habitats within the site will also contribute to improving water quality by taking-up waterborne nutrients as water passes onto and through the site. | |||
The Parks Trust will operate and maintain the site as a nature reserve open to the general public. This will enable the local community and visitors from further afield to experience the diverse floodplain forest habitat and the wildlife it attracts. | |||
A further benefit of the project is that under the Trust’s charitable remit, the income it received from the gravel sales form the site have been reinvested back into the establishment and care of this environmental project. | |||
With the involvement of Cranfield University, the floodplain forest will be more widely promoted as a case study in habitat creation and restoration techniques and as an on-going subject for scientific monitoring and research. In summary there are a range of ecosystem services provided by the floodplain forest: cultural, regulating and other services. | |||
}} | |||
{{Image gallery}} | |||
{{Case study image | |||
|File name=Floodplain Forest 1.jpg | |||
}} | |||
{{Case study image | |||
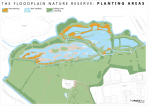
|File name=Floodplain-nr---planting-plan.png | |||
}} | |||
{{Image gallery end}} | |||
{{Toggle button}} | |||
{{Toggle content start}} | |||
{{Case study subcatchment | |||
|Subcatchment=Great Ouse (Upper) | |||
}} | |||
{{Site | |||
|Name=Floodplain Forest | |||
|WFD water body code=GB105033037920 | |||
|Heavily modified water body=No | |||
|Protected species present=No | |||
|Invasive species present=No | |||
}} | |||
{{Project background | |||
|Project started=2007/01/01 | |||
|Project completed=2014/01/01 | |||
}} | |||
{{Motivations | |||
|Hydromorphological quality elements=Encourage natural functioning of the floodplain during flood conditions | |||
|Biological quality elements=Long term vision to increase biodiversity in Milton Keynes | |||
|Other motivation=Integrate wildlife and society | |||
}} | |||
{{Measures | |||
|Floodplain / River corridor=Removal of sand from beneath agricultural fields and restoring marsh lands has increased floodplain capacity and improved floodwater management | |||
|Social measures=Improved public access, Bird watching area | |||
|Wider stakeholder / citizen engagement=Information board erected, | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{Hydromorphological quality elements header}} | |||
{{End table}} | |||
{{Biological quality elements header}} | |||
{{End table}} | |||
{{Physico-chemical quality elements header}} | |||
{{End table}} | |||
{{Other responses header}} | |||
{{End table}} | |||
{{Monitoring documents}} | |||
{{Monitoring documents end}} | |||
{{Additional Documents}} | |||
{{Additional Documents end}} | |||
{{Additional links and references header}} | |||
{{Additional links and references footer}} | |||
{{Supplementary Information}} | |||
{{Toggle content end}} | |||
Latest revision as of 16:52, 21 February 2018
Project overview
| Status | Complete |
|---|---|
| Project web site | http://www.theparkstrust.com/parks/floodplain-forest |
| Themes | Environmental flows and water resources, Habitat and biodiversity, Hydromorphology, Monitoring, Water quality |
| Country | England |
| Main contact forename | Natalia |
| Main contact surname | Perez-Linde |
| Main contact user ID | User:NataliaLinde |
| Contact organisation | Cranfield University |
| Contact organisation web site | http://www.cranfield.ac.uk/about/media-centre/news-archive/news-2014/floodplain-restoration-project.html |
| Partner organisations | The Parks Trust, Environment Agency, EPSRC (Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council), Hanson Cement |
| Parent multi-site project | |
| This is a parent project encompassing the following projects |
No |
Project summary
The Manor Farm Floodplain Forest and its associated PhD research project is a best practice example of bringing together industry (Hanson), a charitable body (The Parks Trust), non-departmental public body (Environment Agency) and academia (Cranfield University). The Parks Trust (land owner) joined forces with Hanson (quarry operator) with the vision of creating this new floodplain forest landscape along of a 1 km reach of the River Great Ouse. It was the first project of its kind in United Kingdom where planning permission was obtained specifically for the creation of a floodplain forest habitat.
The Parks Trust owns over 2000 hectares of parkland around Milton Keynes and continually seeks to improve their parks by providing new facilities, increasing biodiversity and enhancing habitats. The Trust joined with Cranfield University to establish a PhD research project to develop a hypothesis-driven adaptive monitoring framework for assessing the environmental outcomes of the Floodplain Forest, as a case study with application to ecological management. Outputs of this research have enhanced understanding of the aspects to consider when assessing floodplain forest re-creation/restoration and have been used to develop guidelines for land managers based on a long-term monitoring approach. These management guidelines will be applicable to other similar restoration projects.
Community Involvement - bird-watching areas and information boards provided to encourage local interest in the area.
Monitoring surveys and results
The Parks Trust engaged Cranfield University to help establish a monitoring and evaluation strategy for the floodplain forest. As well as monitoring environmental variables the Trust will instigate market research and community engagement programmes to assess the effect of the developing habitat on how local people and visitors from further afield use and perceive the site.
Cranfield University aimed to assess the habitat outcomes in the floodplain forest after quarry works finished. We have designed an adaptive monitoring framework in order to assess key variables (i.e. creating a baseline for further comparisons over time after restoration works finished). The key variables selected for restoration appraisal are soil, water table, vegetation, water quality and topography. We complement the AMF with a hypothesis (The ratio between vegetation associated with wet and dry soils within the floodplain forest and its associated river is determined by the site topography and the water table level) and study the water table level interaction with tree species in a glasshouse experiment. Results gathered in the experiment will be extrapolated to the field to assess the suitable habitats planting according to water table availability and topography in the floodplain forest.
Lessons learnt
The project has increased the capacity and flood retention capacity of the floodplain by removing a volume of around 700,000 tonnes of mineral reserves. Some of this volume has been replaced by standing water but under non-flood conditions the standing water lies at lower level that the former ground.
The project has also created better connection between the River Great Ouse and the pre-existing and new channels that have been created in the site. As the river level rises, water can flow into the site (i.e. floodplain) via these channels, thereby receiving floodwater that would previously have put pressure on more developed/built-up areas further down the Ouse Valley, such as Newport Pagnell which has a number of known flood risk areas near the River Ouse.
The complex of channel sand low-lying landforms within the site, including gravel banks, sand bars and small islands provides a varied floodplain habitat that will mature into a diverse ecosystem supporting a wide range of plants and insects, amphibians, birds, fish and mammals such as otter and water vole. The habitats within the site will also contribute to improving water quality by taking-up waterborne nutrients as water passes onto and through the site.
The Parks Trust will operate and maintain the site as a nature reserve open to the general public. This will enable the local community and visitors from further afield to experience the diverse floodplain forest habitat and the wildlife it attracts.
A further benefit of the project is that under the Trust’s charitable remit, the income it received from the gravel sales form the site have been reinvested back into the establishment and care of this environmental project.
With the involvement of Cranfield University, the floodplain forest will be more widely promoted as a case study in habitat creation and restoration techniques and as an on-going subject for scientific monitoring and research. In summary there are a range of ecosystem services provided by the floodplain forest: cultural, regulating and other services.
Image gallery
|
Catchment and subcatchmentSelect a catchment/subcatchment
Catchment
Subcatchment
Site
Project background
Cost for project phases
Reasons for river restoration
Measures
MonitoringHydromorphological quality elements
Biological quality elements
Physico-chemical quality elements
Any other monitoring, e.g. social, economic
Monitoring documents
Additional documents and videos
Additional links and references
Supplementary InformationEdit Supplementary Information
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||