Case study:Tarrant Monkton Rehabilitation Project: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Case study status | {{Case study status | ||
|Approval status= | |Approval status=Approved | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Location | {{Location | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|Main contact surname=Guest | |Main contact surname=Guest | ||
|Main contact id=RachelM | |Main contact id=RachelM | ||
|Contact organisation= | |Contact organisation=Environment Agency | ||
|Contact organisation url=www.gov.uk/government/organisations/environment-agency | |Contact organisation url=www.gov.uk/government/organisations/environment-agency | ||
|Multi-site=No | |Multi-site=No | ||
|Project picture= | |Project picture=Tarrant1 Monkton Location.JPG | ||
|Project summary=The work was based on conceptual outline plans provided by Nigel Holmes and Allan Frake working for Casterbridge Fisheries interpreted and supervised the installation of in channel features and woody debris/flow deflectors. | |Project summary=The work was based on conceptual outline plans provided by Nigel Holmes and Allan Frake working for Casterbridge Fisheries interpreted and supervised the installation of in channel features and woody debris/flow deflectors. | ||
The need for a more sustainable solution to the obstruction to fish passage at Manor Farm was identified, alongside opportunities to improve stream habitat and re-energise the watercourse. Habitat enhancements will create a faster, more variable flow regime and a more diverse habitat, which will help to promote a unique range of important animal and plant species. Physical habitat enhancements coupled with good land use management, including appropriate fencing and grazing regimes, will also contribute to achieving good ecological status under WFD. A better quality habitat may help species build resilience to the changes associated with climate change. | The need for a more sustainable solution to the obstruction to fish passage at Manor Farm was identified, alongside opportunities to improve stream habitat and re-energise the watercourse. Habitat enhancements will create a faster, more variable flow regime and a more diverse habitat, which will help to promote a unique range of important animal and plant species. Physical habitat enhancements coupled with good land use management, including appropriate fencing and grazing regimes, will also contribute to achieving good ecological status under WFD. A better quality habitat may help species build resilience to the changes associated with climate change. | ||
|Monitoring surveys and results=Periodic visits to the site will be made to help ensure grazing management is ideal for the conditions that develop. Tree growth or failure to grow should be monitored. Repeat photographs are recommended for the archive. Biological monitoring may be of limited value if pre-conditions have not been recorded. The creation of an accurately scaled diagram of the location and extent of each feature will also facilitate ease of repeating the As Built mapping survey to ascertain how the channel and the installations respond to the various flow and non-flow conditions and how the channel evolves physically and ecologically over time. | |Monitoring surveys and results=Periodic visits to the site will be made to help ensure grazing management is ideal for the conditions that develop. Tree growth or failure to grow should be monitored. Repeat photographs are recommended for the archive. Biological monitoring may be of limited value if pre-conditions have not been recorded. The creation of an accurately scaled diagram of the location and extent of each feature will also facilitate ease of repeating the As Built mapping survey to ascertain how the channel and the installations respond to the various flow and non-flow conditions and how the channel evolves physically and ecologically over time. | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Image gallery}} | {{Image gallery}} | ||
{{Case study image | |||
|File name=Tarrant Monkton Location.JPG | |||
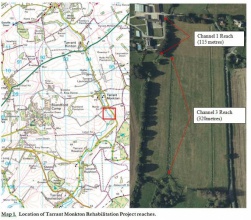
|Caption=Map and photo of location of project | |||
}} | |||
{{Image gallery end}} | {{Image gallery end}} | ||
{{Toggle button}} | {{Toggle button}} | ||
{{Toggle content start}} | {{Toggle content start}} | ||
{{Case study subcatchment}} | {{Case study subcatchment | ||
{{Site}} | |Subcatchment=TARRANT | ||
}} | |||
{{Site | |||
|WFD water body code=GB108043016070 | |||
|WFD water body name=TARRANT | |||
|Heavily modified water body=No | |||
|Protected species present=No | |||
|Invasive species present=No | |||
}} | |||
{{Project background | {{Project background | ||
|Reach length directly affected=413.2 | |Reach length directly affected=413.2 | ||
| Line 31: | Line 43: | ||
|Works completed=2014/10/04 | |Works completed=2014/10/04 | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Motivations}} | {{Motivations | ||
{{Measures}} | |Hydromorphological quality elements=barrier to fish migration | ||
|Biological quality elements=improve in-stream habitats | |||
}} | |||
{{Measures | |||
|Planform / Channel pattern=Flow deflectors, Introducing large woody debris, | |||
}} | |||
{{Hydromorphological quality elements header}} | {{Hydromorphological quality elements header}} | ||
{{End table}} | {{End table}} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:05, 6 June 2017
Project overview
| Status | Complete |
|---|---|
| Project web site | |
| Themes | Environmental flows and water resources, Fisheries, Habitat and biodiversity |
| Country | England |
| Main contact forename | Sarah |
| Main contact surname | Guest |
| Main contact user ID | User:RachelM |
| Contact organisation | Environment Agency |
| Contact organisation web site | http://www.gov.uk/government/organisations/environment-agency |
| Partner organisations | |
| Parent multi-site project | |
| This is a parent project encompassing the following projects |
No |
Project summary
The work was based on conceptual outline plans provided by Nigel Holmes and Allan Frake working for Casterbridge Fisheries interpreted and supervised the installation of in channel features and woody debris/flow deflectors.
The need for a more sustainable solution to the obstruction to fish passage at Manor Farm was identified, alongside opportunities to improve stream habitat and re-energise the watercourse. Habitat enhancements will create a faster, more variable flow regime and a more diverse habitat, which will help to promote a unique range of important animal and plant species. Physical habitat enhancements coupled with good land use management, including appropriate fencing and grazing regimes, will also contribute to achieving good ecological status under WFD. A better quality habitat may help species build resilience to the changes associated with climate change.
Monitoring surveys and results
Periodic visits to the site will be made to help ensure grazing management is ideal for the conditions that develop. Tree growth or failure to grow should be monitored. Repeat photographs are recommended for the archive. Biological monitoring may be of limited value if pre-conditions have not been recorded. The creation of an accurately scaled diagram of the location and extent of each feature will also facilitate ease of repeating the As Built mapping survey to ascertain how the channel and the installations respond to the various flow and non-flow conditions and how the channel evolves physically and ecologically over time.
Lessons learnt
Image gallery
|
Catchment and subcatchmentSelect a catchment/subcatchment
Catchment
Subcatchment
Other case studies in this subcatchment: River Tarrant Rehabilitation Project
Site
Project background
Cost for project phases
Reasons for river restoration
Measures
MonitoringHydromorphological quality elements
Biological quality elements
Physico-chemical quality elements
Any other monitoring, e.g. social, economic
Monitoring documents
Additional documents and videos
Additional links and references
Supplementary InformationEdit Supplementary Information
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||