Case study:River Tarrant Rehabilitation Project: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|Main contact surname=Guest | |Main contact surname=Guest | ||
|Main contact id=RachelM | |Main contact id=RachelM | ||
|Contact organisation= | |Contact organisation=Environment Agency | ||
|Contact organisation url=www.gov.uk/government/organisations/environment-agency | |Contact organisation url=www.gov.uk/government/organisations/environment-agency | ||
|Name of parent multi-site project=Tarrant Monkton | |Name of parent multi-site project=Tarrant Monkton | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Measures | {{Measures | ||
|Bank and bed modifications measure= | |Bank and bed modifications measure=Bed reprofiling, Bank stabilisation, | ||
|Planform / Channel pattern=Flow deflectors | |Planform / Channel pattern=Flow deflectors | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:04, 6 June 2017
Project overview
| Status | Complete |
|---|---|
| Project web site | |
| Themes | Environmental flows and water resources, Habitat and biodiversity, Water quality |
| Country | England |
| Main contact forename | Sarah |
| Main contact surname | Guest |
| Main contact user ID | User:RachelM |
| Contact organisation | Environment Agency |
| Contact organisation web site | http://www.gov.uk/government/organisations/environment-agency |
| Partner organisations | |
| Parent multi-site project | |
| This is a parent project encompassing the following projects |
No |
Project summary
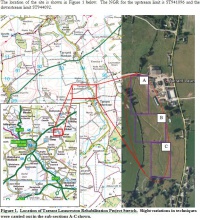
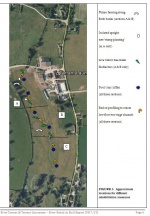
A very uniform 500m section of the Tarrant, with extremely limited existing habitat diversity, was modified using a number of different techniques. The main work involved re-profiling the bed to create some variation in long and cross-section. No re-profiling of banks was undertaken, nor did the work involve any land-take. In the upstream sub-sections A-B live willow logs/stakes were also installed into the river or up the bank slopes in specific locations.
The physical modifications of re-distributing bed material around, installing log deflectors and occasional short stake to form pollards, was completed in just over two days. Work was completed within four days by wiring down firmly each of the installed willow logs and cutting pinning stakes back to log height.
Monitoring surveys and results
Monitoring was completed before works to detirmine where works should be focused.
Monitoring was also completed after the works to establish how successful the project had been.
At the very least periodic visits to the site should be made to help ensure grazing management is ideal for the conditions that develop. Repear photographs are recommended for the archive. Biological monitoring may be of limited value if pre-conditions have not been recorded.
Lessons learnt
Providing cattle and sheep do not have access to the channel on a permanent basis, the created features of pools, runs and low-flow self-cleansing sections will not only be sustained, but improve over time.
The hoped for growth of willow to form both habitat and landscape improvements has less chance of guaranteed success - the logs and stakes have been left far too long (over seven months at least) for ideal use. They have also been installed much later in the season than is the norm to encourage sprouting and rooting. When installed in the dormant period, or spring / early summer, sprouting is accompanied by rapid root growth - both will be limited now, and roots may not have sufficient dampness to succeed.
Keeping the banks fenced for two years will be ideal if any growth of willows is to reachits maximum potential; thereafter periodic grazing will help keep lower branches in check and be good for all other aspects of the marginal vegetation (as well as restore full grazing potential)
Image gallery
|
Catchment and subcatchmentSelect a catchment/subcatchment
Catchment
Subcatchment
Other case studies in this subcatchment: Tarrant Monkton Rehabilitation Project
Site
Project background
Cost for project phases
Reasons for river restoration
Measures
MonitoringHydromorphological quality elements
Biological quality elements
Physico-chemical quality elements
Any other monitoring, e.g. social, economic
Monitoring documents
Additional documents and videos
Additional links and references
Supplementary InformationEdit Supplementary Information
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||