Case study:Albbruck-Dogern (bypass and nature-like pool pass)
Project overview
| Status | Complete |
|---|---|
| Project web site | |
| Themes | Economic aspects, Fisheries, Hydropower |
| Country | Switzerland |
| Main contact forename | Rolf-Jürgen |
| Main contact surname | Gebler |
| Main contact user ID | User:Kasvio |
| Contact organisation | Ingenieurmeinschaft Gruner/Kelag |
| Contact organisation web site | http://www.radag.de |
| Partner organisations | Rhein Kraftwerk Allbruck-Gogern AG, Ing. Büro Kesselring |
| Parent multi-site project | |
| This is a parent project encompassing the following projects |
No |
Project summary
The hydroelectric power plant at the High Rhine is designed as a diversion-channel type. The discharge in the River Rhein is at the moment high, 1610 m3/s (1484 m3/s). The discharge to the fish way is always at the minimum 600 l/s (max 800 l/s). In addition to the main power station (Q = 1000 m³/s) a new second power station (Q = 300 m³/s) was installed at the diversion weir to feed the natural river bed with a sufficient discharge. In the course of this project a permanent near-natural running water, with a length of about 900 m and a discharge of 2-5 m³/s has been installed at the left embankment.
If the discharge in the river is higher than 1200 m3/s then the max discharge is let to the bypass channel.
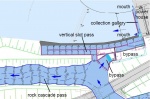
The total height of 10.4 m is established by a near-nature water course with a slope of 0.8% and a steeper downstream end. At the upper end the water course is divided into two arms: the rock-cascade-pass (Q = 0.8-3.0 m³/s) leads straight onto the river bed at the left bank. The second arm, designed as a vertical-clot-pass connects the water course with the tailwater of the turbine outlet. Above the turbine outlet a collection gallery with different fish entrances is installed. The total discharge at the outlet varies between 0.6 m³/s and 4.0 m³/s. The height difference in the fish ladder steps are 20–30 cm.
Before the (re)contruction of the plant there was insufficient residual water flow (3‐8 m3/s) due to the diversion, section for the existing power plant “Albbruck Dogern”, interrupted continuum by river weir, interrupted fish migration, low fish population and low population of aquatic fauna. After the contruction work of the plant there has been immediate increase of the residual water flow: 3.8 m3/s to 40 m3/s; from the 1st January 2008 up to 70‐100 m3/s. Creation of a nature like fish ladder with collection gallery, renaturing of former gravel islands, upvaluation of a birdisland. New weir‐power plant extension uses in operation a water flow of min. 200 m3/s. Implementation of the ecological measures lasted until year 2012. Hydromorfological improvements concerned the connection of the sidewater Alb to the Rhine, creation of a nature like bed structure in the diversion with gravelbars and ecological improvements in the whole area of the river diversion and in the river course under the weir. Also there was ecological improvements of the ecological diversity of the shoreline. Now many migratory fish uses the bypass channel. For example the grayling spawns in the bypass channel.Also the area is open for the residents to walk along the channel. The new chanel is also very attractive for birds and insects.
Monitoring surveys and results
Lessons learnt
Image gallery
|
Catchment and subcatchment
Site
Project background
Cost for project phases
Reasons for river restoration
Measures
MonitoringHydromorphological quality elements
Biological quality elements
Physico-chemical quality elements
Any other monitoring, e.g. social, economic
Monitoring documents
Additional documents and videos
Additional links and references
Supplementary InformationEdit Supplementary Information
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||