Case study:Salzano wetland and Marzenego river restoration project
Project overview
| Status | Complete |
|---|---|
| Project web site | |
| Themes | Flood risk management, Habitat and biodiversity, Land use management - forestry, Monitoring, Social benefits, Water quality |
| Country | Italy |
| Main contact forename | Paolo |
| Main contact surname | Cornelio |
| Main contact user ID | |
| Contact organisation | Consorzio di Bonifica Acque Risorgive |
| Contact organisation web site | http://www.acquerisorgive.it/ |
| Partner organisations | |
| Parent multi-site project | |
| This is a parent project encompassing the following projects |
No |
Project summary
In order to reduce eutrophication problems that severely impair the quality of the Venice lagoon waters, the local government
(the Veneto Region Authority), more than a decade ago,established a series of targets for the the reduction of nutrients that
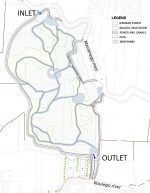
flow into the lagoon. As a detailed example, The “Salzano wetland” restoration was completed by the consortium which was, until the mid-1980s, subject to mining of clay. Since this period this 60 ha site has gradually been restored. Today this site is characterized by a mosaic of habitats of different spatial extent. The main actions of the project were:
a) to create a system of new banks around a dry and with low ecological value portion (20 ha wide) of the extent wetland, and later to connect this area with the adjacent watercourse using gates to manage flows; b) reshaping the net of canals, ponds and pools inside this area to find the optimal residual time of the water to assure an efficient nutrient reduction; c) re-establish rare and endangered aquatic vegetation types (Carex elata, Cladium mariscus, Allium angulosum, Cirsium canum, Senecio paludosus, Typha laxmannii, Iris pseudacorus and Nuphar luteum) and monitor their development; d) create a new net of small channels to connect this restored wetland to the other portions; e) create a net of path and observation structures accessible to the public for recreation, educational and technical-scientific purposes.
Monitoring surveys and results
Lessons learnt
Image gallery
|
Catchment and subcatchmentSelect a catchment/subcatchment
Catchment
Subcatchment
Other case studies in this subcatchment: Pagana canal restoration project, Rio San Martino and Piovega di Scandolara restoration project, Rio Sant'Ambrogio restoration project, Scolo Desolino restoration project, Zero river restoration project
Site
Project background
Cost for project phases
Reasons for river restoration
Measures
MonitoringHydromorphological quality elements
Biological quality elements
Physico-chemical quality elements
Any other monitoring, e.g. social, economic
Monitoring documents
Additional documents and videos
Additional links and references
Supplementary InformationEdit Supplementary Information
Image gallery
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||