Case study:LakeAdmin - Chadwick lakes - Plan to improve the surface water quality and reservoir restoration in the Chadwick lakes area: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
{{Site | {{Site | ||
|Name=Chadwick Lakes | |Name=Chadwick Lakes | ||
|Heavily modified water body= | |Heavily modified water body=Yes | ||
|Protected species present= | |Protected species present=Yes | ||
|Invasive species present= | |Invasive species present=Yes | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Project background | {{Project background | ||
Revision as of 15:34, 12 December 2019
This case study is pending approval by a RiverWiki administrator.
Project overview
| Status | Complete |
|---|---|
| Project web site | |
| Themes | Environmental flows and water resources, Habitat and biodiversity, Social benefits |
| Country | Malta |
| Main contact forename | Temi Zammit Foundation |
| Main contact surname | - |
| Main contact user ID | |
| Contact organisation | Temi Zammit Foundation |
| Contact organisation web site | http://ftz.org.mt |
| Partner organisations | |
| Parent multi-site project | |
| This is a parent project encompassing the following projects |
No |
Project summary
The LakeAdmin Project (Interreg IVC) consists of ten partners from nine countries including Finland, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy and Malta. The LakeAdmin project aims at an exchange of good water management practices to support the implementation of the Water Framework Directive in each of the partner regions and to produce case study collection on restoration and management experiences and water quality data from the relevant lakes in each partner region covering the last 30 years. All participating regions have identified lakes as important elements in their regional development policies.
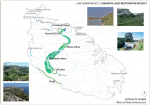
The Chadwick lakes are a succession of artificial dams built by a colonial engineer, known as Sir Oswald Chadwick. This originally man-made environment progressively evolved into a natural haven. The water system represents one of the best examples of rainwater-fed watercourses on the island, and still today, the area still provides a good flood protection and a water service system for the irrigation of fields. Apart from that, the area is a naturalistic spot used for recreational activities. Inland surface and transitional waters often are of great ecological importance because they harbour a number of species and habitats of conservation value. Indeed, many inland waters in Malta have been scheduled as Areas of Ecological and/or Scientific Importance, and are also part of Natura 2000 sites designated under the EU Habitats and Birds Directive. In the case of Chadwick Lakes, there is a significant lack since the area is not scheduled as a Natura 2000 site and is not even present in the water quality assessments carried out by the Water Catchment Management Plan.
The Chadwick Lakes area embodies great naturalistic value and plays an important role in the ecosystem balance of the island. Moreover, is it a tourist/leisure attraction of unique beauty. For a better conservation and restoration of the whole area, a holistic management plan is necessary, together with the update of policies and the implementation of restoration measures.
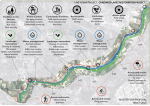
Concepts and overall strategy of the Plan: 1. WATER MANAGEMENT: 1.1. Structural restoration and maintenance of reservoirs 1.2. Natural water purification systems 2. LANDSCAPE RESTORATION: 2.1. Naturalisation of shoreline and watercourse rehabilitation 2.2. Vegetation management plan 3. SITE MANAGEMENT 3.1. Creation of a good system of access points, paths and tracks 3.2. Provision of new facilities addressed to the community and visitors 3.3. Organization of events, environmental education, visits for students, hiking tours 4. MONITORING 4.1. Drafting of a monitoring plan 4.2. Installation of weather stations and water level stations 4.3. Sampling campaigns for monitoring of chemical, physical and biological parameters 4.4. Periodical control on chosen indicators 4.5. Co-operation with University and Analysis Laboratories 5. GOVERNANCE 5.1. Involvement of authorities for the definition of policies and actions 5.2. Organization of workshops and courses involving local farmers and other stakeholders 5.3. Awareness-raising activities targeted to local citizens and schools
Monitoring surveys and results
Lessons learnt
- The Plan is an opportunity not to be missed in order to establish actions and implement targets that can be beneficial for all the territory and also for the Chadwick lakes
- The Maltese Rural Development Plan and its actions represent an important set of tools and means for the implementation of Chadwick lakes Implementation Plan
- By matching Chadwick’s actions with the RDP policy is possible to legitimate and support economically the Chadwick lakes Implementation Plan
- the RDP gives an unique opportunity to strengthen the relations between different stakeholders by enhancing the already established National Rural Network
Possibility to work with the Network: involve all the local actors (farmers, NGOs, Planning Authority) and engage them in a bottom-up participatory process.
Image gallery
|
Catchment and subcatchment
Site
Project background
Cost for project phases
Reasons for river restoration
Measures
MonitoringHydromorphological quality elements
Biological quality elements
Physico-chemical quality elements
Any other monitoring, e.g. social, economic
Monitoring documents
Additional documents and videos
Additional links and references
Supplementary InformationEdit Supplementary Information
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||