Case study:Irpin river restoration: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
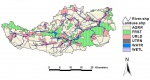
{{Case study image | {{Case study image | ||
|File name=Nitratepaths.png | |File name=Nitratepaths.png | ||
|Caption=Canalisation is still missing. Groundwater pollution from living places is assessed by GIS-based modelling. | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{Image gallery end}} | {{Image gallery end}} | ||
Revision as of 08:49, 2 June 2015
Project overview
| Status | Planned |
|---|---|
| Project web site | |
| Themes | Economic aspects, Flood risk management, Hydromorphology, Land use management - agriculture, Social benefits, Spatial planning |
| Country | Ukraine |
| Main contact forename | Michael |
| Main contact surname | Hoffmann |
| Main contact user ID | User:Miho-kiev |
| Contact organisation | Institute of Water Problems and Land Reclamation |
| Contact organisation web site | http://igim.org.ua |
| Partner organisations | |
| Parent multi-site project | |
| This is a parent project encompassing the following projects |
No |
Project summary
The full name of the project is: Integrated Planning of water resources use within the Irpin River basin, subtitle: Irpin River restoration via integrated river basin management - Balancing nature, agriculture and recreation. The project was presented on the RR conference in Vienna 2013.
The project idea was developed on the basis of results from a comprehensive technical/hydrological study of the whole river basin in the years 2009-2012. In 2013 the Ukrainian Centre for River Restoration (UCRR) was established at the Institute of Water Problems and Land Reclamation, Kiev. The Irpin river project was selected as a first official project of the UCRR.
The project implementation has started with the participation and consultation of stakeholders in a special workshop in April 2014. Before, during and after this workshop all kind of information has been collected and used to set up a database for the use of GIS visualisation, GIS-based modelling and first characterisation of the catchments.
Monitoring surveys and results
A regular monitoring as foreseen for the WFD was not yet implemented. Existing results of former studies are mainly related to river discharge and random samplings for water quality controls. Further monitoring results are collected by several departments of the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources of Ukraine. The sampling stations are however further downriver of the subbasin border.
Lessons learnt
The big number of problems and open questions is beyond the personnel and financial capacity of Ukrainian state institutions. International cooperation will help to gain or exchange best practices in river restoration but it is also clear that a much smaller subbasin of the river had to be selected to start with.
Image gallery
|
Catchment and subcatchment
Site
Project background
Cost for project phases
Supplementary funding informationThe project is still in the planning phase; funds not yet available
Reasons for river restoration
Measures
MonitoringHydromorphological quality elements
Biological quality elements
Physico-chemical quality elements
Any other monitoring, e.g. social, economic
Monitoring documents
Additional documents and videos
Additional links and references
Supplementary InformationEdit Supplementary Information
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||